Table of Contents
Multisubject
Support for multisubject C3D files allows users to easily work with datasets that include more than one subject in a dynamic trial, for example, two people sparring or dancing within the capture volume. It's expected that subject prefixes are used in the C3D files. For example, a target is named “S001:LMK” where “S001:” is the subject prefix and “LMK” is the target name (note: most camera manufacturers already support this option).
For the static trial, the multiple subjects can be in the same C3D file, or in multiple static C3D files.
Notes
- If only collecting data with one subject in the volume, nothing about your processing procedure should change and you should not export C3D files with subject prefixes from your camera manufacturer.
- If you had a subject in one static trial, and a bench in another static trial. The two static trials can be associated and the segments in both trials will be created in the dynamic trials. If you are collecting data for one subject with multiple static trials, go here for more information.
- This documentation refers mostly using the multi-subject workspace with two subjects, however, you can use as many subjects as you would like.
Important Terms
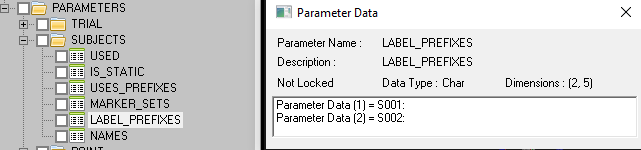
Subject Prefix: In the C3D file, there is a parameter to specify the subject prefix. This should be specified by your motion capture system. Subject prefixes can be different from C3D file to C3D file
Subject Tag: A subject tag associates a generic name to a subject prefix, for example “Ball-carrier” or “Tackler”. The active Subject Tag can be set using the Select_Active_File pipeline command.
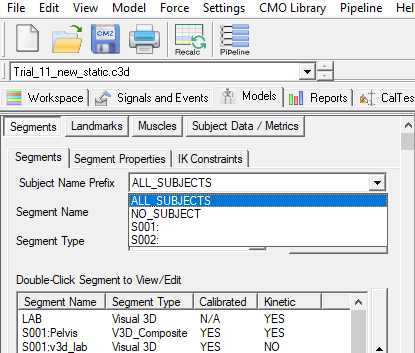
Model Tab
Within the Model Builder tab the user can choose between the following options for active subject: ALL_SUBJECTS, NO_SUBJECT, and any individual subject prefix.
| Selection | Description |
|---|---|
| ALL_SUBJECTS | Allows you to view all segments with subject prefixes |
| NO_SUBJECT | Allows you to view all segments not associated with a subject prefix (ex. LAB) |
| Subject prefixes | Allows you to view all segments associated with that subject prefix. |
Pipeline
The first step to writing a pipeline is to assign a subject tag to a subject prefix using the Set_Subject_Tag command. This is important since a subject prefix can be different for each data collection (ex. “S001:”, “S002:”). The subject tag should be something general (ex. “Pitcher”, “Catcher”). Once the subject tags have been defined, you can use the subject tags the same as you would a file tag using the Select Active File command.
As with single subject files, the resulting pipeline commands will work on the active subject tags that were specified in the Select Active File command
Important Pipeline Commands
Pipeline commands that are specifically important for multi-subject data or have been modified for this new feature include:
- Set_Subject_Tag: Sets subject tags for specific files
- Select_Active_File: Use subject tags to precisely specify your active files
- Modify_C3D_Subjects_Parameters: Modify the parameters in the SUBJECTS group in the c3d file
Examples
Example 1: Building Multi-subject Models
The compute model-based command works the same for multiple subjects as it always has for single subjects, but now also allows the customer to use Subject_Tags to identify when signals should be calculated for every subject in the model, between subjects, etc.
Note: Segment A and Segment B tag refer to the Segment tag, or Reference Segment or Resolution Coordinate System.
Case 1: Signal created for all subjects. Ex. RKneeAngle
- Subject tag: ALL_SUBJECTS
- Segment A Tag: ALL_SUBJECTS
- Segment B Tag: ALL_SUBJECTS
Case 2: Signal created for all subjects relative to a segment that is only created in NO_SUBECT (ex. subject's foot relative to generic segment BOX).
- Subject tag: ALL_SUBJECTS
- Segment A Tag: ALL_SUBJECTS
- Segment B Tag: NO_SUBJECT
Case 3: Signal created for one subject between segments that exist in that subject.
- Subject tag: SUBJECT_TAG_NAME
- Segment A Tag: SUBJECT_TAG_NAME
- Segment B Tag: SUBJECT_TAG_NAME
Case 4: Signal created for one subject relative to another subject.
- Subject tag: SUBJECT_TAG_NAME
- Segment A Tag: SUBJECT_TAG_NAME
- Segment B Tag: DIFFERENT_SUBJECT_TAG_NAME